The year 2025 has brought significant advancements to the PC gaming landscape, but it has also introduced immense complexity. Choosing the wrong component can severely limit your rig’s potential, turning a powerhouse PC into a bottlenecked frustration. The single most important decision for a gaming computer remains the graphics card. It is the engine that drives frame rates, powers immersive visuals, and determines your overall gaming experience.
This Best Graphics Cards 2025 guide is engineered to cut through the marketing noise. We provide a complete, informative, and definitive look at the current market, comparing the high end dominance of Nvidia RTX and AMD Radeon cards against the practical realities of budget GPUs. Whether you are targeting crystal clear 4K gaming or seeking the best possible price to performance ratio for 1080p, this guide offers the insights needed to make an informed upgrade decision for the year ahead.
The Best Graphics Cards of 2025 Our Top Picks
The GPU market in 2025 is structured around performance tiers that directly correlate with your target screen resolution. While every system is unique, these recommendations represent the current pinnacle of performance and value available across the spectrum. We have focused heavily on maximizing frame rates while considering the cost of entry and long term utility.
Overall Champion The 4K Performance Beast
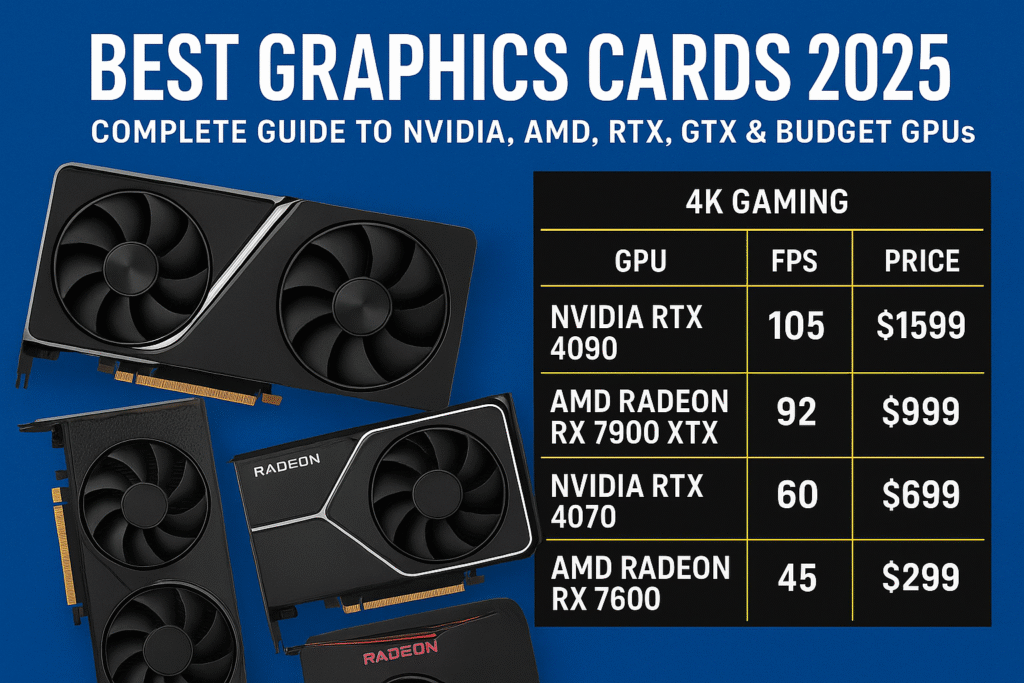
For the uncompromising gamer who demands maximum detail and high refresh rates at 4K resolution, the best option remains the reigning king of the high end segment. This card offers unmatched raw power, particularly in demanding titles that utilize intensive Ray Tracing effects. Its massive pool of VRAM ensures texture detail is never sacrificed, and proprietary acceleration technologies, like the newest iteration of Nvidia DLSS, provide essential performance boosts. It is a substantial investment, but it guarantees a top tier experience well into the future, making it the most future proof graphics card on the market.
The 1440p Sweet Spot Balancing Power and Affordability
The middle tier is arguably the most competitive, as 1440p (or QHD) remains the most popular resolution for serious PC builders. The perfect choice in this category must offer excellent frame stability at competitive settings without breaking the bank. This segment is where the concept of the price to performance ratio is most keenly felt. Currently, an upper mid range card from either Nvidia or AMD Radeon dominates this space, offering enough processing power and memory (typically 12GB to 16GB) to manage high refresh rates. This card is highly recommended for users running 144Hz to 240Hz monitors, providing an outstanding balance of visual quality and responsiveness.
Best Value Graphics Card for 1080p The Budget King
Not every gamer requires 4K mastery; many players prioritize competitive frame rates at the standard 1080p resolution. In this scenario, affordability and efficiency are key. We recommend a specific, highly optimized entry level GPU that manages to deliver consistent 60+ FPS in modern AAA titles and much higher frame rates in competitive esports games. This card excels by being power efficient and having a low purchase price, making it an ideal choice for first time builders or those upgrading from very old hardware. It proves that you do not need to spend a fortune to enjoy modern PC gaming.
Nvidia RTX vs. AMD Radeon A 2025 Showdown
The competitive rivalry between the two main GPU giants—Nvidia and AMD—is fiercer than ever in 2025. Each company offers distinct advantages, and the “better” choice depends entirely on the user’s priority raw rasterization speed or advanced feature ecosystems.
Core Architecture & Performance Ada Lovelace vs. RDNA 3 and Beyond
Nvidia’s current architecture e.g., Ada Lovelace, powering the RTX 40 Series is designed for maximum efficiency and feature integration. It tends to deliver superior performance in games that push the graphical envelope. Conversely, AMD’s RDNA 3 architecture found in the Radeon RX 7000 Series often prioritizes raw rasterization throughput, which translates to better general performance in traditional rendering at a given price point. For sheer peak performance and proprietary technology, Nvidia often leads; for pure frame per dollar value, AMD frequently holds an advantage in certain tiers.
The Upscaling War Deep Dive into DLSS vs FSR and Frame Generation
Upscaling technology is arguably the most crucial innovation of this decade. It allows GPUs to render games at a lower resolution and intelligently reconstruct the image to match a higher target resolution.

Nvidia Deep Learning Super Sampling DLSS
Utilizes dedicated Tensor Cores and an AI network. This generally results in superior image clarity and minimal artifacts. DLSS 3, in particular, introduced Frame Generation, which inserts entirely new, synthesized frames, dramatically boosting perceived frame rates.
AMD FSR FidelityFX Super Resolution
An open source solution that works across a wider range of hardware, including older Nvidia and even integrated graphics. While FSR 3 now includes its own form of Frame Generation, it is generally considered to be slightly behind DLSS in final image quality, though its broader compatibility is a major selling point.
Practical Tip: If you game often in 4K gaming and want the best image quality alongside massive frame rate boosts, prioritize a card with strong DLSS support.
Ray Tracing and Rasterization Who Wins?
Ray Tracing performance simulates how light interacts with objects, creating incredibly realistic shadows, reflections, and global illumination. While both companies support it, Nvidia has a commanding lead due to its dedicated RT Cores. If you want to enable Ray Tracing in demanding titles while maintaining playable frame rates, an Nvidia RTX card is currently the necessary investment. However, if you prefer traditional rasterization (standard rendering) for maximizing FPS, the performance gap between the brands narrows considerably.
Decoding Graphics Card Specifications What Really Matters?
Understanding the spec sheet of a graphics card can feel like reading a foreign language. However, a few key metrics directly impact your gaming experience, especially when comparing different models for your target resolution.
VRAM Video Memory How Much Do You Need?
VRAM is the high speed memory the GPU uses to store essential data like textures, frame buffers, and geometry. Insufficient VRAM leads to stuttering and massive performance drops, especially at higher resolutions and settings.
| Resolution | Recommended VRAM (2025) | Why it Matters |
| 1080p | 8GB | Comfortable for high settings, future proof for new releases. |
| 1440p | 12GB 16GB | Essential for texture caching in open world games and utilizing higher quality upscaling. |
| 4K | 16GB+ | Necessary to manage the immense texture and framebuffer size required by 4K gaming. |
Clock Speeds, Cores, and Bus Width
- Clock Speed: Measured in MHz or GHz, this is how quickly the GPU processes instructions. Higher is generally better, but always compare speeds within the same architecture.
- Cores/Stream Processors: The engine of the GPU. Nvidia uses CUDA Cores; AMD uses Stream Processors. A higher count usually equates to more raw processing power.
- Bus Width: Measured in bits (e.g., 192 bit, 256 bit). This is the path between the GPU chip and the VRAM. A wider bus allows for much faster data transfer, which is critical for pushing high resolutions like 4K.
TDP, Power Consumption, and Your PSU
TDP (Thermal Design Power) and overall power consumption are vital factors often overlooked. Modern high end GPUs are extremely power hungry, requiring a robust Power Supply Unit (PSU) and adequate case cooling. A powerful graphics card like a top tier RTX model might require a dedicated 850W or even 1000W PSU, which adds to the total build cost. Always check the manufacturer’s recommended PSU wattage before purchasing. High TDP also means more heat generation, necessitating larger coolers and potentially a larger PC case.
Buying on a Budget Best Value and Entry Level GPUs
The mid range and budget graphics cards market is exceptionally dynamic, making it a minefield for the unprepared shopper. Success here hinges on finding the optimal balance between cost and current gaming needs.
Price to Performance Kings
The goal for any budget graphics card buyer is maximizing the frames you get per dollar spent. While the flagship models capture attention, many cards in the $300 to $500 range offer excellent 1080p and capable 1440p performance. These GPUs typically feature 8GB to 12GB of VRAM and are highly efficient. They are the clear best GPU for 1080p gaming and represent the smarter financial choice for the majority of mainstream PC users. They are the definition of the mid range GPU performance benchmark.
Is a GTX Still Viable in 2025?
For the extreme budget conscious, particularly those interested only in esports or older titles, the legacy GTX series (like the GTX 1660 Super) might still surface in the used market. However, with modern titles increasingly requiring features like Ray Tracing and at least 8GB of VRAM, the GTX architecture is reaching its functional obsolescence. While technically playable, they lack the hardware acceleration necessary for modernNvidia DLSS and Frame Generation, severely limiting their longevity. A contemporary, cheaper AMD Radeon card or a lowerend current generation RTX card is almost always a better investment for future proofing.
The Used Market Risks and Rewards
The used GPU market can offer significant savings, but it comes with risk. You can secure a powerful previous generation card e.g., an older RTX 30 series at a steep discount.
Tips for buying second hand:
- Check Warranty: See if the original manufacturer’s warranty is transferable.
- Proof of Purchase: Request the original receipt to confirm the purchase date.
- Ex Mining Cards: Avoid cards heavily used for cryptocurrency mining, as they often have degraded fans and potentially shorter lifespans due to continuous, high heat operation.
Gaming Resolution Tiers Finding the Right Graphics Card

Matching your GPU to your monitor’s resolution is the most critical step in building a balanced system. The power needed increases exponentially as you move from 1080p to 4K.
Uncompromising 4K Gaming
Required Hardware: Flagship Nvidia RTX or high end Radeon cards.To maintain frame rates above 60 FPS in modern, graphically intensive titles at 4K resolution (3840 x 2160) without relying exclusively on upscaling, you need maximum processing power, a wide memory bus, and plenty of VRAM. This is the realm of the $800+ best GPU for 4K gaming. These cards are designed for large screens, high fidelity textures, and maximizing immersion through features like Ray Tracing.
The Perfect 1440p Experience
Required Hardware: High end mid range cards or last generation flagships.1440p (2560 x 1440) offers a significant visual upgrade over 1080p while remaining achievable for most high end consumer hardware. The mid range GPU performance leaders in 2025 are tailored for this resolution. They are powerful enough to drive 144Hz refresh rates, especially when using Frame Generation techniques, providing competitive performance that feels incredibly smooth and responsive.
Maxed Out 1080p Gaming
Required Hardware: Budget to mid range cards.
1080p (1920 x 1080) gaming has evolved. The latest games still stress budget hardware, particularly on Ultra settings. However, modern 8GB budget graphics cards from both Nvidia and AMD are more than capable of achieving high, competitive frame rates (100+ FPS) in almost any title. These cards provide the best value proposition and are perfectly suited for competitive gamers who prioritize responsiveness over graphical excess.
Future Proofing Your PC 2025 Trends and Considerations
A graphics card purchase is an investment meant to last several years. You must consider emerging trends and potential hardware limitations to ensure your new card remains relevant.
The CPU Bottleneck Matching Your New GPU to the Right Processor
A common mistake is pairing a powerhouse GPU with an outdated or underpowered CPU. This results in a phenomenon known as GPU bottlenecking, where the CPU cannot feed the GPU data quickly enough to reach its full potential. For example, pairing a new high end RTX card with a six year old mid Range CPU will waste performance and money. Aim to match your GPU to the corresponding CPU tier High end GPU with a high end CPU e.g., Intel i7/i9 or Ryzen 7/9 mid range GPU with a mid range CPU e.g., Intel i5/i7 or Ryzen 5/7.
PCIe 5.0 and Beyond Is the New Standard Essential?
PCI Express (PCIe) is the connection interface between the motherboard and the GPU. While current high end graphics cards utilize the PCIe 4.0 standard, newer motherboards and some GPUs now support PCIe 5.0. Currently, the performance difference between a PCIe 4.0 and a PCIe 5.0 connection is negligible for nearly all cards, as the 4.0 standard offers more than enough bandwidth. Should I upgrade to PCIe 5.0 in 2025? For now, no, unless you are building a top tier rig designed for several generations of future upgrades.
Drivers and Longevity Which Brand Offers Better Support?
Driver stability and updates are paramount for long term ownership.
- Nvidia is generally known for frequent, timely driver updates, particularly with major game launches, and excellent application support for creative suites.
- AMD has significantly improved its driver ecosystem in recent years, often bringing substantial performance gains to older cards through optimization.
Choosing a card that is expected to receive support for at least 4 5 years is a key part of future proof graphics card planning. Both companies are committed to their current generation of products, offering confidence to buyers.
Conclusion
Choosing the Best Graphics Cards 2025 requires careful consideration of budget, resolution target, and desired features like Ray Tracing or Frame Generation. The market is defined by performance tiers Flagship Nvidia RTX cards dominate the 4K segment, while mid range AMD Radeon and Nvidia cards offer superb mid range GPU performance and value at 1440p.
The key takeaway is to invest in enough VRAM (12GB minimum for 1440p and higher) and to always check your PSU requirements. By understanding the competitive edge of DLSS versus FSR and matching your GPU to your monitor and CPU, you can secure a powerful and future proof graphics card that will drive incredible gaming experiences for years to come. Start building the ultimate PC with your chosen graphics card today.for more usefull informatn visit this article GPU Benchmarks 2025 Performance Comparison of All Popular Models
FAQ Section
What is the best graphics card for 1440p 144Hz gaming in 2025?
The current mid to high end cards from both Nvidia and AMD are ideal. Focus on models with 12GB or more VRAM that support either DLSS or FSR 3 for enhanced frame rates at 144Hz.
How much VRAM do I really need for new games in 2025?
We recommend a minimum of 8GB for 1080p, 12GB for comfortable 1440p, and 16GB or more for high fidelity 4K gaming. Running out of VRAM causes severe stuttering.
Are Nvidia’s DLSS and AMD’s FSR essential features now?
Yes. With game requirements increasing, these upscaling technologies, especially Frame Generation, are critical for maintaining high frame rates at high resolutions. Your future proof graphics card must support one of them.
When is the best time to buy a graphics card?
GPU prices fluctuate significantly. Historically, prices often drop after major product launches (Q4) or during large retail events (Black Friday/Cyber Monday). Avoid buying right after a major new release.
What is GPU bottlenecking and how can I avoid it?
Bottlenecking occurs when your CPU is too slow to send data to your GPU efficiently. Avoid it by pairing a high end GPU with a contemporary high end CPU and a mid range GPU with a mid range CPU
Should I upgrade to PCIe 5.0 in 2025?
While PCIe 5.0 offers future bandwidth, most current graphics cards do not saturate the PCIe 4.0 standard. An upgrade is not strictly necessary for performance right now, but it’s a good feature for long term motherboard investment
What is the best entry level/budget GPU for 2025?
Look for the latest generation’s entry level models offering 8GB of VRAM. These are the most power efficient and cost effective ways to achieve smooth 1080p performance