The world of PC building and gaming is constantly evolving, and the most critical component is undoubtedly the graphics card. For years, Nvidia‘s GTX line reigned supreme. However, the introduction of RTX shifted the paradigm entirely, creating confusion for many buyers. This guide is designed to clarify the essential differences, dissect the underlying technology like Ray Tracing and DLSS, and provide a complete, clear cut buyer’s roadmap. By the end, you’ll fully understand Nvidia Graphics Cards Explained RTX vs GTX Full Buyer’s Guide and know exactly which card best suits your needs, whether you’re a gamer, a creative professional, or a budget conscious builder.
The Core Difference Architecture and Features
The primary distinction between the RTX and GTX lines lies in their underlying GPU architecture and the specialized cores they contain. GTX cards, like the 16 series, rely solely on traditional CUDA Cores for rasterization—the process of taking 3D models and turning them into 2D pixels on your screen. RTX cards, which began with the Turing architecture and continue with Ampere and Ada Lovelace, include two crucial, specialized components RT Cores and Tensor Cores. These additions make the RTX line future proof and feature rich.
What are the key technological advancements in RTX?
The RTX line introduced hardware acceleration for features that were computationally impossible for GTX cards. The most significant are Ray Tracing and DLSS. The dedicated RT Cores handle complex lighting calculations, while the Tensor Cores are specifically designed for machine learning, which powers the revolutionary DLSS technology. These specialized processing units are the fundamental reason RTX cards deliver a dramatically different level of visual fidelity and performance efficiency.
GTX vs. RTX A Feature Comparison Table
| Feature | Nvidia GTX (e.g., 16 Series) | Nvidia RTX (e.g., 40 Series) |
| Primary Technology | Rasterization | Ray Tracing & Rasterization |
| Dedicated Ray Tracing Cores | No | Yes (RT Cores) |
| Dedicated AI/DLSS Cores | No | Yes (Tensor Cores) |
| DLSS Support | No | Yes (Gen 2, 3, 3.5) |
| Focus | High Frame Rate at Base Graphics | High Fidelity & Performance Scaling |
Why the “R” in RTX Matters Dedicated Cores
The “R” in RTX stands for Ray Tracing. While GTX cards can attempt some basic ray tracing through software emulation, they lack the dedicated RT Cores that handle the complex calculations efficiently. Without these cores, the performance hit from activating Ray Tracing on a GTX card is often too severe to be practical for gaming. The inclusion of dedicated RT Cores on every RTX GPU ensures that this next generation lighting and reflection technology can be run smoothly.
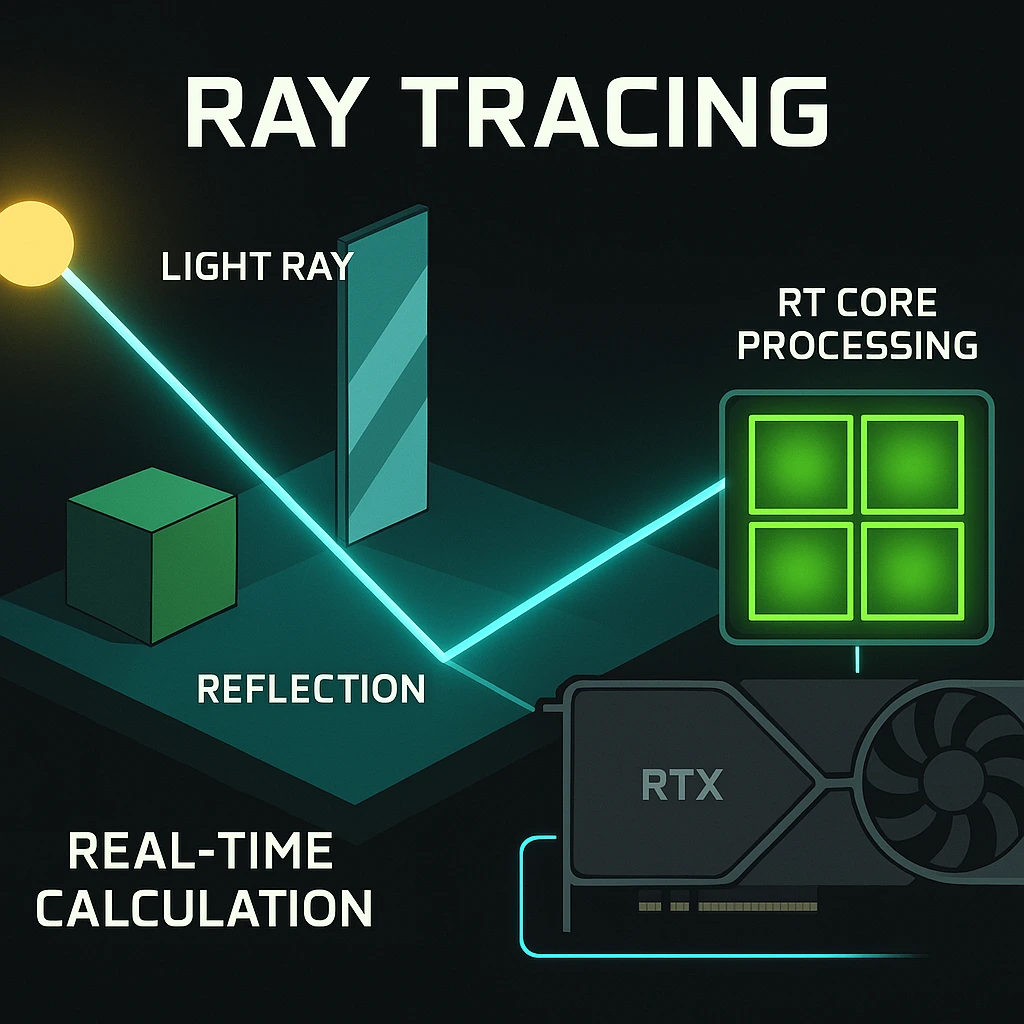
A Deep Dive into Ray Tracing The Cinematic Upgrade

Ray Tracing is a rendering technique that simulates the physical behavior of light. Instead of using pre baked or simplified lighting effects, it tracks individual “rays” of light as they bounce off objects in a scene. The result is hyper realistic shadows, reflections, and global illumination that bridge the gap between video games and cinematic CG. This level of realism adds significant depth and atmosphere to supported titles.
What exactly is Ray Tracing and how does it work?
In simple terms, Ray Tracing is the most accurate way to model light in a 3D environment. The RT Cores on an RTX card are optimized to rapidly calculate these light paths. For instance, in a scene with a reflective floor, the RTX card tracks the light, calculates the reflection accurately, and projects it onto the surface in real time. This is exponentially more complex than the rasterization method used by GTX cards.
Do GTX cards support hardware accelerated Ray Tracing?
No, GTX cards do not offer true hardware accelerated Ray Tracing. While Nvidia did enable a software implementation of Ray Tracing on some higher end GTX cards, the performance trade off is often crippling. It’s essentially a demonstration of the technology, not a playable experience. The dedicated RT Cores found only in RTX cards are mandatory for a modern, enjoyable Ray Tracing experience.
Is Ray Tracing a must have feature in today’s games?
While not strictly required, Ray Tracing is rapidly becoming an expected feature in AAA titles. Modern games are built with it in mind, and enabling it provides a superior, more immersive visual experience. While a GTX card will still play most games, it will be locked out of this visual upgrade. For a true next gen feel, an RTX card is necessary.
DLSS Explained Free Performance for RTX Owners
DLSS is arguably the most critical feature of the RTX line for gamers. Standing for Deep Learning Super Sampling, this technology uses the dedicated Tensor Cores to intelligently upscale a lower resolution image to a higher resolution output. The result is image quality that often rivals or exceeds native resolution, but with significantly increased frame rate (FPS). This performance boost mitigates the cost of enabling graphically intensive settings like Ray Tracing.
How does DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling) boost frame rate?
DLSS works by rendering a game at a lower resolution (e.g., 1080p) and then using an Nvidia trained, AI model to reconstruct a high resolution image (e.g., 1440p or 4K). Because the GPU renders fewer pixels, the workload is drastically reduced, leading to much higher FPS. The Tensor Cores handle the upscaling with incredible speed and accuracy, resulting in a gaming performance gain that feels like getting a free hardware upgrade.
What are the different DLSS modes Quality, Balanced, Performance?
Users can typically choose from several DLSS modes
- Quality: Highest image fidelity, moderate FPS gain.
- Balanced: Good mix of image quality and FPS increase.
- Performance: Maximum FPS gain, lowest input resolution (can result in some visual artifacts).
- Ultra Performance: Designed for very high resolution 4K or 8K setups.
Which RTX generations support the newest DLSS versions?
All RTX cards (starting with the 20 series Turing architecture) support DLSS. However, the newer generations (30 series Ampere and 40 series Ada Lovelace) support advanced versions like DLSS 3, which includes Frame Generation. This revolutionary technique creates entirely new, interpolated frames, further doubling the frame rate in some titles. This feature is a game changer for pushing high resolution, high fidelity gaming.
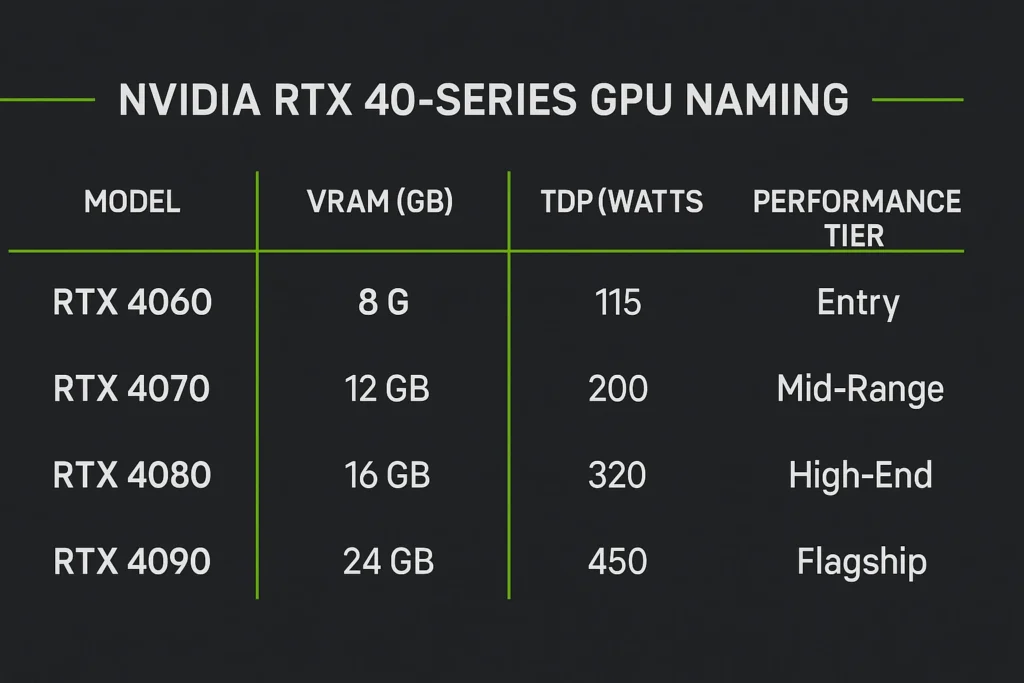
Decoding Nvidia’s Naming Convention and GPU Hierarchy
When comparing any Nvidia graphics card, you’ll see a series of numbers and suffixes that are key to understanding its place in the market. Knowing this scheme helps you quickly determine a card’s relative performance level and generation.
Understanding the Series and SKU e.g., 4070, 3060 Ti
Nvidia‘s naming convention is straightforward
- First two digits (or three for older cards): The Series or Generation. (e.g., 40 in RTX 4070 means 40 series).
- Last two digits (The SKU): The performance tier. Lower numbers are entry level (e.g., 50), mid range is 60/70, and high end is 80/90.
- Suffixes: Ti (Titanium) indicates a slightly faster, upgraded version of the base model (e.g., RTX 4070 Ti is faster than a 4070). SUPER also indicates an enhanced version.
VRAM and TDP Essential Specs for Gaming Performance
Two technical specifications are crucial for comparing cards
- VRAM (Video Memory): This is the GPU‘s dedicated memory, measured in Gigabytes (GB). More VRAM is essential for high resolution (1440p and 4K) and high texture gaming. For modern gaming, 8GB is a baseline, and 12GB+ is safer for future proofing.
- TDP (Thermal Design Power): Measured in Watts (W), this indicates the maximum heat generated, which directly correlates to the card’s power draw. Higher TDP cards require larger power supplies and better cooling in the PC case.
What is the difference between a Founders Edition and a Partner card?
The Founders Edition is Nvidia‘s own reference design, sold directly. AIB Partner (Add in Board) cards are made by companies like ASUS, MSI, and Gigabyte. The internal GPU is the same, but the AIB Partner cards often feature custom cooling solutions, factory overclocks for slightly better gaming performance, and unique aesthetics. Both types are generally excellent, but partner cards can offer better thermal efficiency.
RTX vs. GTX for Non Gaming Workloads and Content Creation
While gaming dominates the conversation, the shift from GTX to RTX is even more profound for creative professionals. The specialized cores that power Ray Tracing and DLSS also dramatically accelerate production tasks.
How CUDA Cores benefit video editing and rendering
Both GTX and RTX cards utilize Nvidia‘s CUDA Cores for parallel processing, which is used by creative applications like Adobe Premiere Pro and Blender. However, RTX cards feature a much higher density of these cores in their modern architectures, providing exponential gains. Furthermore, the Tensor Cores can be used for AI driven tasks within creative suites, like noise reduction or smart upscaling, significantly reducing rendering times.
Which card is better for AI, Machine Learning, and streaming?
The RTX line is unequivocally superior for these tasks. The dedicated Tensor Cores are specifically designed for the matrix math used in machine learning (AI/ML) and are a requirement for high speed training and inference. For streaming, all modern Nvidia cards include a dedicated encoder (NVENC), but the newer versions found in the RTX series offer superior quality and lower system overhead, allowing streamers to maintain a high frame rate while broadcasting.
A look at the value proposition for workstations
For professional users who rely on software like AutoCAD, Maya, or DaVinci Resolve, an RTX card is an investment that pays for itself in time saved. The speed increase in rendering complex scenes or applying high end effects dramatically boosts productivity. Even if you’re not gaming, the non gaming benefits of RTX are immense, making legacy GTX cards a poor choice for serious content creation.
The Ultimate Nvidia Graphics Card Buyer’s Guide by Resolution
Choosing the right card ultimately comes down to your budget and the resolution of your monitor, as resolution is the primary factor driving a GPU‘s workload.
Best RTX and GTX options for 1080p gaming
For 1080p (Full HD) at high refresh rates, you don’t necessarily need a top tier card.
- Entry/Mid Range: An older, high end GTX card (like a GTX 1660 SUPER) or an entry level RTX card (like an RTX 3050/4060) is sufficient.
- Recommendation: An RTX 4060 offers excellent 1080p performance, plus DLSS 3 to ensure smooth frame rate in future titles.
Recommended cards for 1440p and competitive gaming
1440p is the sweet spot for many USA gamers, requiring a more powerful GPU.
- Mid to High Range: You should look at the mid to upper tier RTX cards (e.g., RTX 3070 Ti or RTX 4070). These cards have the necessary VRAM and processing power to handle the increased pixel count.
- Competitive Gaming: For high refresh rate competitive titles, the combination of a powerful RTX card and DLSS is essential to push frames well above 144 FPS. Advanced Competitive Gaming Setup Guide
When do you absolutely need a flagship card for 4K?

4K resolution gaming is the most demanding workload. To achieve a stable, playable frame rate (60 FPS+) at high settings, especially with Ray Tracing enabled, you need a flagship RTX card.
- Flagship Tier: This includes cards like the RTX 4080 and RTX 4090. These models have massive VRAM pools and the most powerful Tensor Cores to make DLSS a necessity for a smooth experience. A flagship card is the only way to genuinely enjoy a beautiful 4K experience without significant compromises.For an in depth performance analysis focusing on value in the high end tier, read the RTX 4080 vs. RTX 4070 Ti Best Value GPU Comparison.
Conclusion
The evolution from GTX to RTX represents a generational leap in graphics technology, not just a simple name change. The introduction of RT Cores for Ray Tracing and Tensor Cores for the revolutionary DLSS fundamentally separates the two lines. While GTX cards remain a budget option for 1080p rasterization gaming, RTX is the mandatory path for anyone seeking cutting edge visual fidelity, superior gaming performance, and accelerated productivity. Use this complete guide to confidently choose between Nvidia Graphics Cards Explained RTX vs GTX (Full Buyer’s Guide) and build the perfect PC for your future needs.
FAQ Section
Is RTX just a new name for GTX?
No, RTX is a completely different architecture. RTX cards contain specialized RT Cores (for Ray Tracing) and Tensor Cores (for DLSS and AI), which GTX cards do not have. The performance and feature set are vastly different.
Can GTX cards run Ray Tracing?
Technically, yes, via software emulation on higher end GTX models, but the massive drop in frame rate makes it unplayable. True, hardware accelerated Ray Tracing is exclusive to the RTX line.
How much faster is DLSS in games?
DLSS can boost frame rate by 50% to over 200%, especially when using DLSS 3 with Frame Generation. The exact gain depends on the game, the resolution, and the DLSS mode selected.
Which RTX card is the best value for money right now?
The best value generally shifts, but the RTX 4070 series (including the Ti or SUPER variants) often provides the best balance of 1440p performance, VRAM, and price for the modern gamer in the USA.
Should I upgrade my old GTX 10 series card to a new RTX card?
Yes, an upgrade from any GTX 10 or 16 series to a modern RTX card (like the 40 series) will provide a massive generational leap in gaming performance, power efficiency (TDP), and access to game changing features like DLSS and Ray Tracing.



